MSF is continuing to provide medical care, including for trauma, and mother and child care, in areas throughout northern Iraq.
Mosul
Inside Mosul City
MSF opened a 15-bed, 24/7 free-of-charge maternity hospital in Karama, in east Mosul, on the 19 March. Since then, the MSF team made up of both expat and Iraqi midwives and obstetricians has assisted 200 women to give birth safely.
MSF opened a 24/7 emergency room in Al Taheel hospital on 26 March. The team has also set up a surgical unit (with one operating theatre currently running, but a second will soon be online), and a 32-bed post-operative ward in order to provide medium-term care to those suffering from violent trauma injuries in and around Mosul. People with older injuries in need of surgical care, surgical follow up, and other types of surgical issues are also treated in this facility. Since opening, over 330 patients have been received in the emergency room, and 30 surgical interventions have been carried out.
In north-east Mosul, MSF works in a hospital set up inside a former retirement home. The ER opened in February, and has been running 24/7 since 1 March providing emergency, surgery, and maternity services (including caesarean sections), and an in-patient department (IPD) with 50 beds. Since the opening of the hospital until early May, the MSF team has treated 4,376 patients, over half of whom (2,286) were urgent cases, and 93 caesarean sections were performed since the maternity unit opened. As the level of access to healthcare is improving in East Mosul, the hospital has seen a drop in activities in the past weeks, especially in terms of lifesaving medical care. As a result, MSF is re-evaluating the project strategy.
Outside Mosul City
Hammam al-Alil is the closest internally-displaced persons (IDP) camp to the south of Mosul, and is located around 30km south of the current frontline. The town has received a big influx of IDPs from western Mosul since start of the military offensive, with more people arriving every day and settling in different camps in the area, or are sent elsewhere after they are screened by security forces.
MSF opened a field trauma hospital with emergency room, two operating theatres, an ICU/recovery room, and IPD on 16 February; for more than one month this hospital was the closest surgical facility to West Mosul. The emergency room received 2,689 patients from 19 February to 19 May, with more than half of them women and children, and more than two-thirds were war-wounded. So far the team has performed 245 major surgical procedures and 56 minor procedures.
Since 15 April, MSF has been supporting the local Department of Health’s primary healthcare centre (PHCC) in Hamman al-Alil, and had already carried out a total of 12,232 consultations by 19 May for both the local population and the IDPs hosted in the community. In the PHCC we perform dressings for wounded patients, including those still being followed up after being discharged from our trauma centre. In Hammam al-Alil, MSF also runs an ambulatory therapeutic feeding centre for children suffering from malnutrition, with a rapidly increasing cohort made up primarily of small babies aged less than six months.
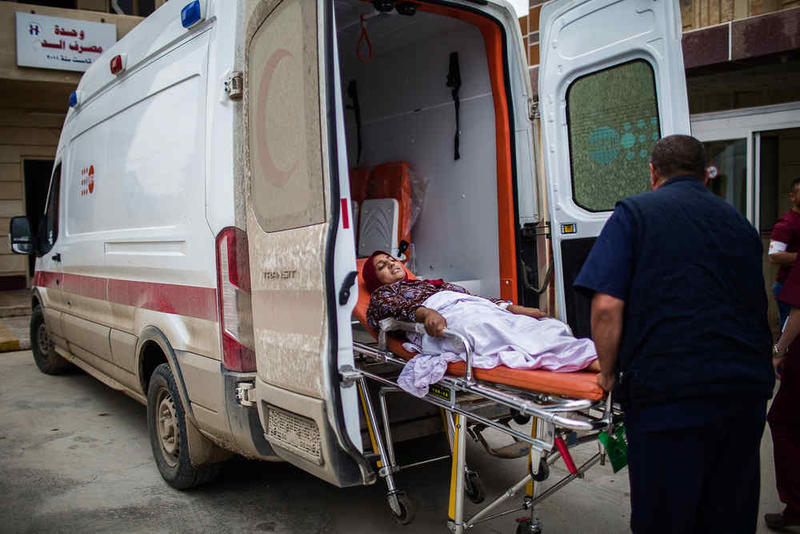
A patient arrives by ambulance at the MSF post-operative hospital, south of Mosul, Iraq.
MSF is providing long-term post-operative care with rehabilitation and psychosocial support in Al Hamdaniya hospital, in collaboration with Handicap International. Activities started on 15 March and to date, MSF has admitted 189 patients, nearly half of whom were women and children. The facility now has 40 beds in order to respond to the huge need for post-operative care and is almost constantly full, receiving new patients who need post-operative follow-up as soon as those who complete their follow-up are discharged.
In December, MSF opened a 32-bed hospital in Quayyarah, 60 km south of Mosul, with an ER and an operating theatre to provide surgical and emergency medical care. The facility has now been extended to cater for the growing and diversifying needs. The team has treated 6,000 patients in the ER as of 1 May, around 10% of whom were admitted to the in-patient department which currently has a 50 bed capacity. A total of 1,130 surgical interventions have been performed since December 2016 until 1 May. A four-bed intermediate care unit was opened in mid-April to provide care to patients in critical condition, and seven observational beds and two resuscitation beds are also now available.
In March, MSF set-up a 12-bed intensive therapeutic feeding centre (ITFC) in Quayyarah to provide care to children recently displaced from west Mosul or Shirkat region, as well as those from IDP camps in Hammam al-Alil and Quayyarah. The majority of the patients in the ITFC are less than six months old. The centre regularly works over capacity and during one week in late May had three babies per bed.
Since February, MSF has been running a mental health clinic for patients admitted to the hospital, as well as for patients referred from Quayyarah camps. The team includes a psychiatrist, two psychologists, and two psychosocial counsellors.
Camps for displaced people
Following the offensive launched into West Mosul in mid-February, the total population of the four camps west of Erbil hosting internally displaced people from Mosul sharply increased to 80,000 people by the end of March. Soon after, the displaced people started leaving the camps to move in with relatives, or rent houses in retaken areas of East Mosul, and the overall population decreased to approximately 70,000.
Today, mobile MSF teams are providing primary health care, treatment for chronic diseases (mainly diabetes and hypertension), as well as psychological and psychiatric care in two of these camps, Chamakor and M2. Activities in M2 are currently more focused on care for non- communicable diseases, with MSF planning to handover primary health care activities by the end of May. MSF has already handed over the treatment of non-communicable diseases in Debaga camp, given the number of IDPs leaving and starting to return to their homes or moving in with relatives in East Mosul.
A team of a psychiatrist, psychologists, and counsellors is also providing health care to those suffering from moderate to severe mental health conditions. Activities include psychological and psychiatric consultations, group therapy, psychosocial counselling, and child therapy. MSF teams currently provide mental health care across 14 sites, and are always extremely busy.
Since the beginning of the year, the team has carried out more than 15,000 medical consultations and 9,000 mental health consultations in the IDP camps near Mosul.
Hawija
Hawija District, one of the four districts of Kirkuk governorate, remains the second largest territory controlled by Islamic State (IS) in Iraq, but the timeline leading to the military intervention to retake the area is not yet known. Hawija is surrounded by more than 200 rural villages and the entire district combined had an estimated population of 288,000 in June 2014, but a large proportion has now reportedly fled.
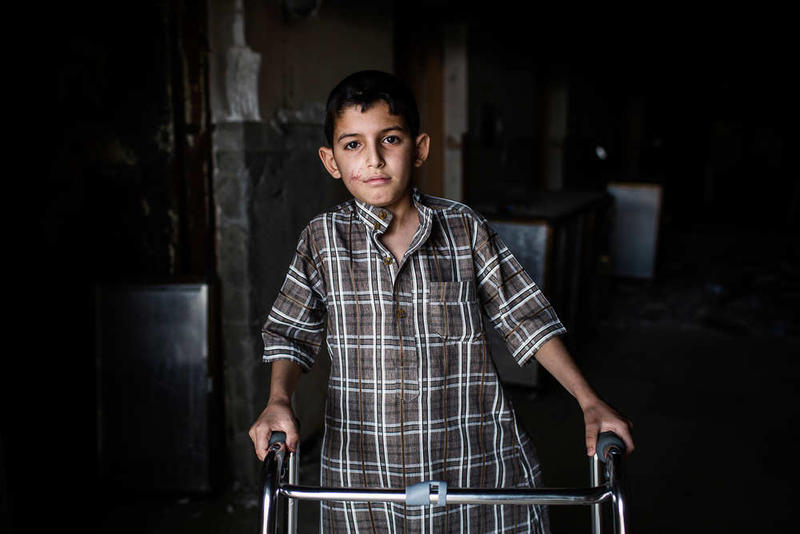

A portrait of 11 year-old Mohamed from West Mosul at the MSF post-operative hospital, south of Mosul, Iraq.
In late 2015, increasing numbers of civilians began fleeing the hardship of life under IS and in June 2016, a militia group cut the last trade road, isolating the district from other IS-held territories and from the rest of Iraq. Since then, living conditions have become dire for the estimated 70,000 people remaining in Hawija district. Due to the siege, food is scarce and prices have skyrocketed. Health facilities have been damaged by airstrikes and local looting, and both health workers and medical supplies (drugs, equipment, and materials) are drastically lacking. It is expected that the military offensive will further disrupt access to basic services and worsen the already critical humanitarian situation.
Of the estimated 88,000 IDPs that have reportedly left Hawija since August 2016, around half are displaced within Kirkuk Governorate, where the vast majority live in Kirkuk’s six IDP camps. A further 30,000 have fled to neighbouring Salah Al-Din governorate. People reported that the main reason for leaving is the lack of food and drinking water.
Since November 2016, MSF has been operating two mobile clinics at Maktab Khalid checkpoint and at Debes screening site to respond to the immediate needs of those fleeing Hawija. Primary health care, first aid, psychological trauma care, and referrals to Kirkuk hospital ER are being provided. MSF has also renovated the water and sanitation facilities in the two sites and distributes water. In Daquq IDP Camp, MSF runs a non-communicable diseases clinic and mental health activities. MSF also supports the emergency rooms of the two main Kirkuk hospitals and has conducted emergency response workshops including specific training on how to deal with injuries to the abdomen and chest, as well as on advanced trauma responses in preparation for mass casualties which may arrive as a result of any future Hawija offensive.





